The reception of aircraft-generated Automatic Dependent Surveillance-Broadcast (ADS-B) signals by satellites in low Earth orbit will allow surveillance of aircraft over regions not covered by radar, such as oceans and the high Arctic.
An RMC ADS-B receiver was launched into a 690 km sun synchronous orbit on 26 September 2016 on the CanX-7 nanosatellite (10 × 10 × 34 cm, 3.5 kg) as a technology demonstrator for space-based monitoring of air traffic.
The satellite also contains a 4 m2 drag sail that will demonstrate accelerated deorbiting.
The ADS-B aircraft tracking receiver will be tested over a six-month period at which point the drag sail will be deployed.
For more information, please visit the Space Flight Laboratory.
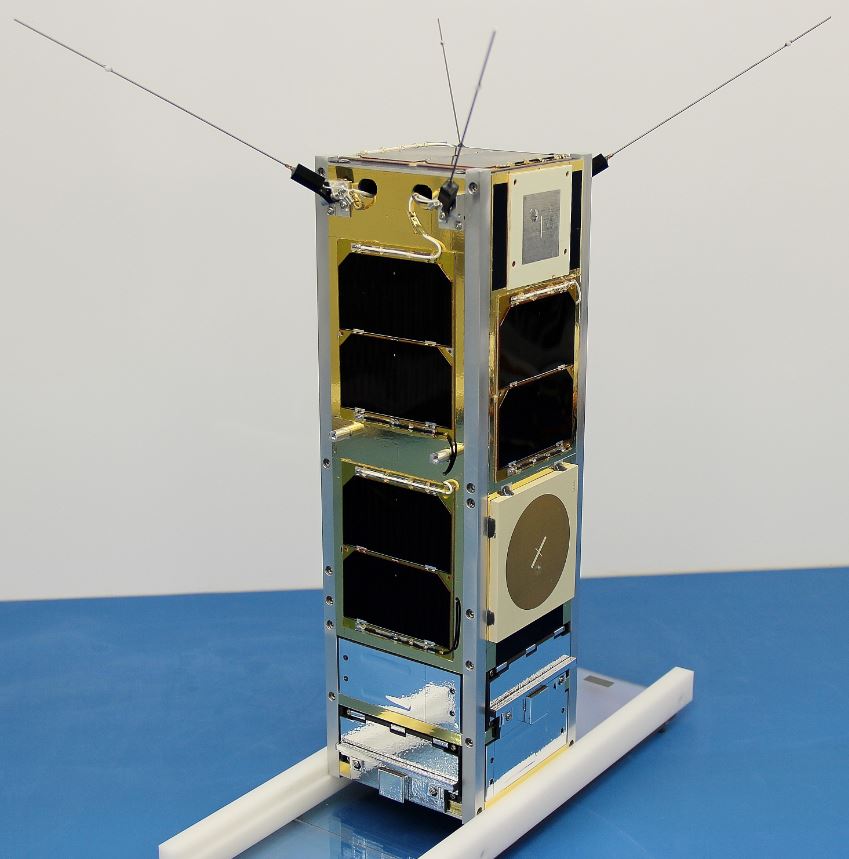 CanX-7 nanosatellite
CanX-7 nanosatellite
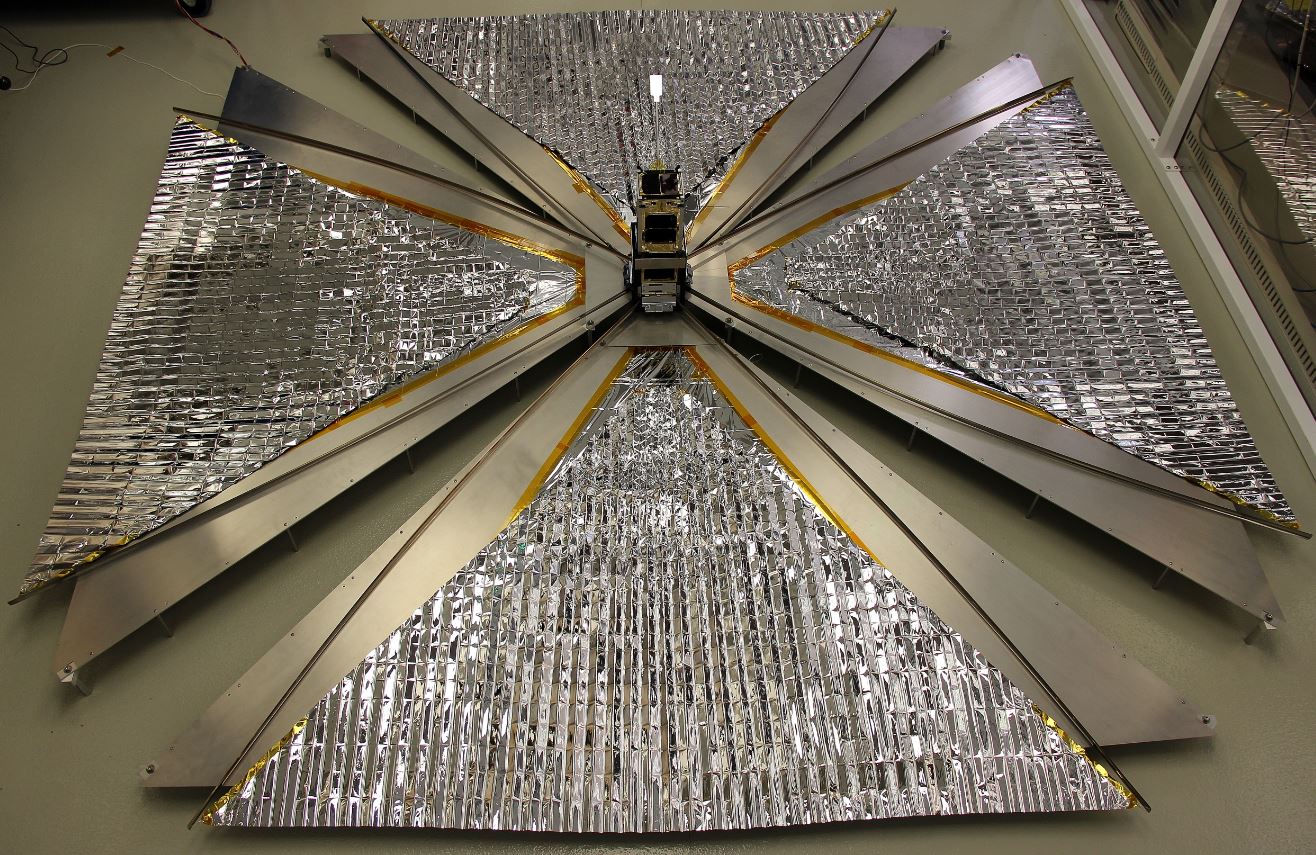 CanX-7 with drag-sail deployed
CanX-7 with drag-sail deployed
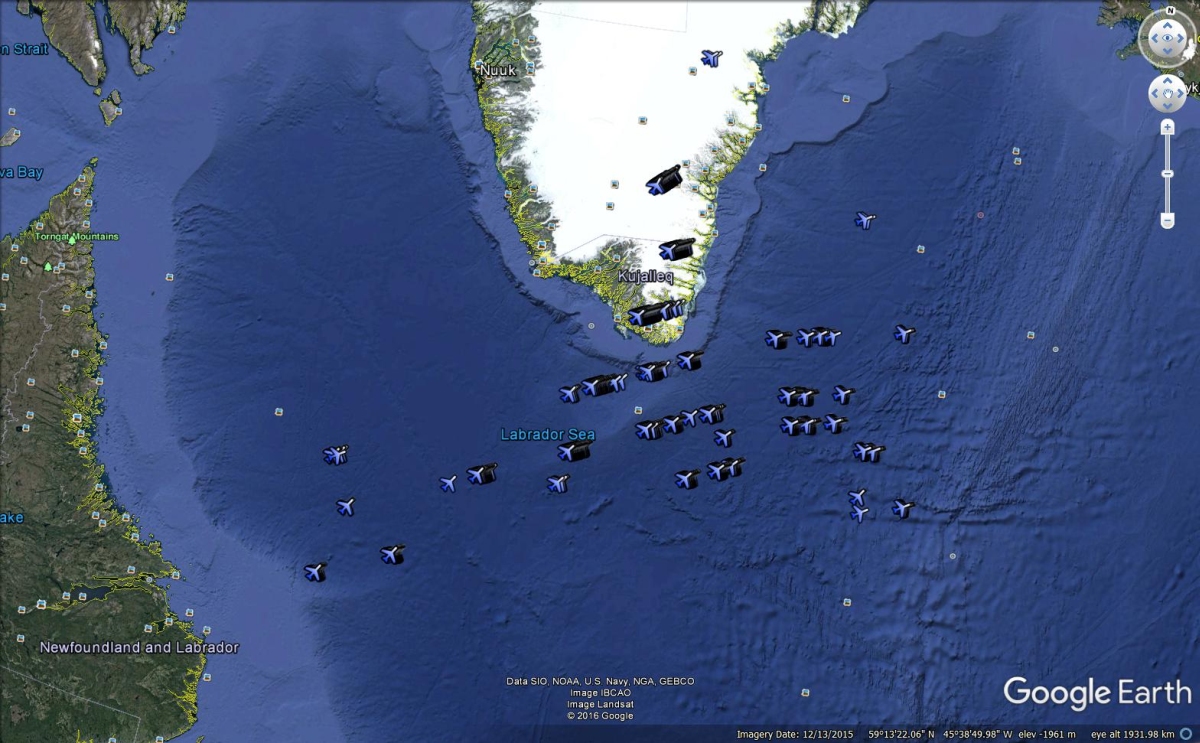 ADS-B data from CanX-7 showing aircraft over the North Atlantic, 28 Sept 2016 (map © 2016 Google, data © Government of Canada)
ADS-B data from CanX-7 showing aircraft over the North Atlantic, 28 Sept 2016 (map © 2016 Google, data © Government of Canada)